For most businesses today, technology plays a central role in daily operations. From communication and collaboration to data storage and customer service, reliable IT systems are essential. However, without a dedicated IT team, handling these systems internally it can quickly become overwhelming.
When staff are pulled away from their roles to deal with IT issues, productivity suffers. Unplanned downtime, slow systems, and security risks all create barriers that stop your team from working efficiently. Over time, these disruptions can affect not just performance but overall business growth.
This is where a managed IT service becomes valuable. Rather than waiting for things to break, managed services focus on preventing issues before they happen. They ensure your systems are maintained, monitored, and supported consistently, helping you reduce risk, avoid downtime, and give your team the tools and confidence to do their jobs effectively.
What Is a Managed IT Service – and Why It’s More Than Just Tech Support
A managed IT service is an ongoing partnership where a third-party provider takes responsibility for monitoring, maintaining, and supporting a business’s technology. Instead of relying on ad hoc repairs or internal staff to fix problems as they arise, businesses gain consistent support that keeps systems running efficiently.
This approach reduces downtime, strengthens security, and helps teams work without interruptions. It includes everything from helpdesk support and system updates to strategic planning and cloud services. By covering both day-to-day issues and long-term IT needs, a managed service takes the pressure off internal teams.
More importantly, it’s not just about fixing problems, it’s about preventing them. A managed IT service helps businesses stay ahead of potential issues, improve system performance, and align their technology with their broader goals.
When IT runs smoothly, people work better. That’s the real value behind managed services.
What You Actually Get With a Managed IT Service
A managed IT service includes more than just reactive support. It covers a full range of services designed to keep your systems secure, reliable, and aligned with how your business operates.
Proactive Monitoring and Maintenance
Your systems are monitored around the clock to catch issues early. Regular maintenance helps prevent outages, slowdowns, and performance drops before they impact your team.
Unlimited Helpdesk Support
When problems do arise, fast and friendly help is only a call or ticket away. Whether it’s a forgotten password or software not loading, your staff can get back to work quickly with expert support.
Cybersecurity Management
Security risks are constantly evolving. A managed service includes cybersecurity protection like firewalls, antivirus, multi-factor authentication, and backup systems to help keep your data safe and your operations secure.
Cloud Services and Microsoft 365
Modern businesses rely on cloud platforms to stay flexible and productive. Managed services include setup and ongoing support for tools like Microsoft 365, cloud storage, and remote access solutions.
Strategic IT Planning
Technology should support your growth, not slow it down. Managed services include regular reviews and planning sessions to make sure your IT systems match your business goals and can scale with your needs.
IT Project Support
When it’s time to upgrade systems, onboard new tools, or improve your setup, a managed IT provider can plan and deliver projects with minimal disruption to your business.
Signs You’re Ready for a Managed IT Service
Not every business starts with managed IT support, but there’s a point where managing tech internally starts to cost more than it saves. If you’re seeing any of the signs below, it may be time to make the switch.
Frequent IT Problems
If you’re dealing with the same issues over and over – like slow systems, dropped connections, or security warnings, it’s a sign your current setup isn’t keeping up.
Staff Handling IT on the Side
When employees are pulled away from their actual jobs to troubleshoot IT problems, productivity drops. It also increases the risk of errors or missed updates.
No Long-Term IT Plan
If your technology setup has grown without structure, it may be holding your business back. Managed IT services can help you build a plan that supports future growth.
Security Concerns
Outdated systems and weak protections leave your business open to threats. Managed IT services ensure you have up-to-date security measures in place.
Growing or Changing Business Needs
Whether you’re hiring more staff, opening new locations, or moving systems to the cloud, a managed IT service can support you through the change without added stress.
Why Businesses Choose Grassroots IT for Managed Services
At Grassroots IT, we don’t take a one-size-fits-all approach. We take the time to understand how your business works so we can provide support that fits your team, your systems, and your goals.
Our Brisbane-based team becomes an extension of your business, offering reliable support with a personal touch. From day one, we focus on building a strong relationship, not just delivering a service. That means clear communication, fast response times, and a consistent commitment to helping your team succeed.
We partner with trusted platforms like Microsoft and HP to ensure the solutions we provide are reliable, secure, and built to support your growth.
When your technology works, your people work better. That’s what we’re here to support – every day.
Let’s Help Your Team Thrive
Managing technology shouldn’t be a distraction. With the right support, your systems can run smoothly, your team can stay productive, and your business can grow without unnecessary delays or risks.
Grassroots IT is here to help make that happen. We work as a true partner, offering managed IT services that support your goals, remove roadblocks, and keep your business moving forward.
Want to see how it could work for your team? Get in touch with us today.
“Is this AI thing actually worth our time, energy and investment?” It’s a question we hear from business leaders when evaluating Microsoft Copilot. The answer isn’t about chasing the latest trend—it’s about identifying where Copilot delivers genuine business value.
When used strategically, Microsoft Copilot unlocks far more than productivity—it becomes a catalyst for innovation and growth.
As technology advisors, we’ve identified three practical ways to use Copilot that help teams work smarter, communicate better, and drive meaningful results.
1.Crafting Strategic Prompts for Targeted Outcomes
The foundation of effective Copilot utilisation lies in developing clear, purposeful instructions. When your prompts lack precision, the resulting output may fall short of your expectations.
Best Practices for Business-Focused Prompts:
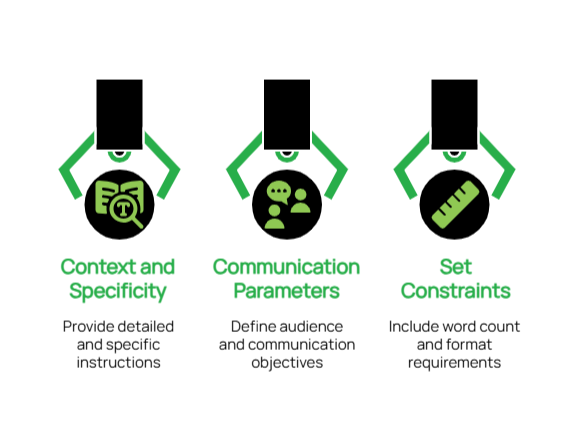
- Provide Context and Specificity: Rather than requesting “write a business email,” specify “create an email announcing our upcoming system maintenance to clients, explain the benefits and include a timeline of what to expect”.
- Define Communication Parameters: Clearly state your intended audience and purpose. For example, “Draft an email to our team explaining the new project management software, focusing on how it simplifies collaboration and what they need to do before launch day”.
- Set Appropriate Constraints: Include practical parameters such as word count limits or specific formats that align with your business needs.
Real-World Applications:
A Non-Profit Organisations: Prompt: “Use Microsoft Copilot to build a checklist in Microsoft 365 that automates thank-you emails to donors. Include steps to personalise messages based on donation amount, connect with our donor database (e.g., Excel or Dynamics 365), and add tracking to measure email engagement like open and click rates.“
Why it works:
This prompt clearly tells Copilot what to automate, how to personalise, and what metrics to track — all within tools non-profits already use.
An Engineering Firm: Prompt: “Write a procedure using Copilot to pull out key specifications from technical documents. Ask it to keep all measurements accurate, highlight any important compliance rules, and point out possible design issues.”
Why it works:
Engineers can quickly get the info they need without missing critical details, helping projects move faster and safer.”
A Medical Practices: Prompt: “Create a Copilot template that turns complex medical procedures into easy-to-read patient handouts. Ask it to keep all medical facts accurate but explain them in plain language that patients can understand.”
Why it works:
Patients feel more informed and confident, and staff spend less time rewriting the same explanations.
This foundation of precise, context-rich prompting transforms Copilot from a generic assistant into a strategic partner that understands your specific industry requirements and delivers consistently relevant results.
2. Develop an Iterative Collaboration Strategy
Think of Copilot as a collaborative partner rather than a one-time tool. By having back-and-forth conversations with it, you’ll refine your ideas and create better content.
Effective Collaboration Techniques:
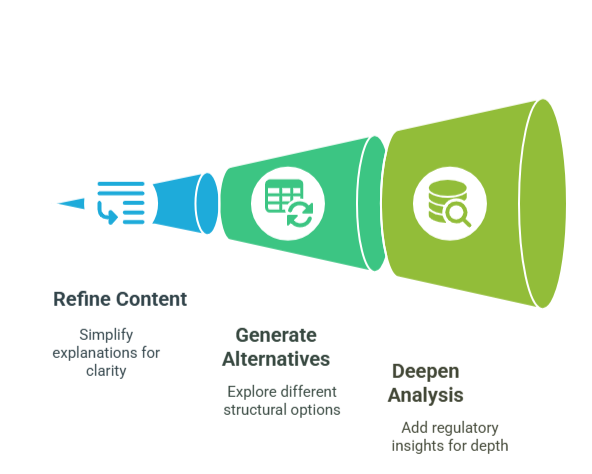
- Refine Content Progressively: When initial output needs improvement, guide Copilot with specific feedback: “Simplify this explanation and use more straightforward language that non-technical users can easily understand.”
- Generate Alternative Approaches: Explore different options by asking: “Show me three different ways we could structure this quarterly business review presentation for our board members.”
- Deepen Analysis: Enhance your documentation with prompts like: “Expand this section to include specific regulatory requirements that apply to our industry and how our solution addresses each one.” For accuracy, you might paste the regulatory requirements sourced from a reliable directory straight into the tool.
Practical Examples:
For Service-Based Businesses (consulting, healthcare, professional services):
Initial Request: “Draft an email template reminding clients about their upcoming appointments.”
Follow-up Refinement: “Revise the template to include a brief explanation of how coming prepared benefits them and what documents they should bring.”
Final Enhancement: “Add a friendly section about our rescheduling policy that emphasises flexibility while reducing last-minute cancellations.”
For Project Documentation:
Initial Request: “Create an outline for our monthly project status report.”
Follow-up Refinement: “Expand the ‘Challenges’ section to include more thoughtful questions about resource allocation.”
Final Enhancement: “Add a forward-looking section that helps team members anticipate next month’s priorities based on current progress.”
This collaborative methodology ensures that your initial ideas evolve into polished, professional communications that align with your strategic objectives and resonate with your intended audience.
3. Elevate Existing Business Documentation and Communications with Seamless Copilot Integration
One of Copilot’s most valuable capabilities is its ability to optimise your existing content, ensuring clarity, consistency, and strategic alignment across all business communications.
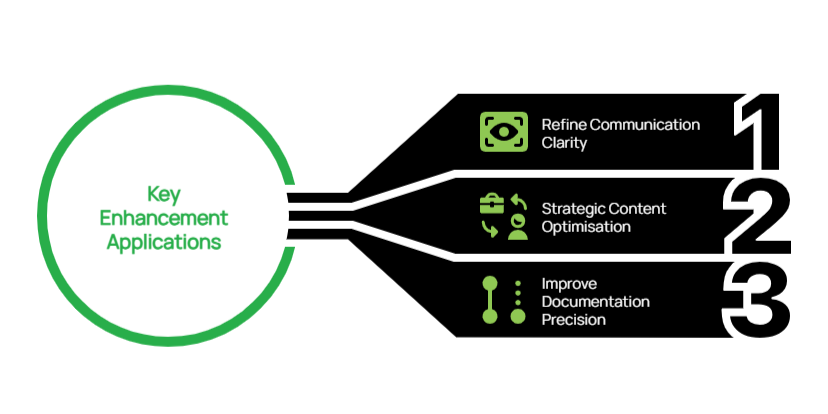
Key Enhancement Applications:
- Refine Communication Clarity: Request improvements to technical documentation with instructions like “Simplify this network assessment report for our client’s leadership team while preserving the essential technical findings”
- Strategic Content Optimisation: When updating client-facing materials, specify “Revise this managed services overview to emphasise business continuity benefits and long-term value rather than just technical specifications”
- Improve Documentation Precision: Enhance operational documentation with requests such as “Review this disaster recovery plan for clarity, completeness, and actionable steps for non-technical users”
Demonstrated Value:
For Non-Profit Leadership: Original Content: “Here’s the volunteer schedule for next month.”
Enhancement Prompt: “Improve this schedule with a more engaging introduction paragraph that thanks our volunteers and explains how their time contributes to our mission.”
Enhanced Output: “Thank You for Your Dedication! This schedule represents more than just dates and times—it’s a roadmap for community impact. Each shift you serve directly supports our mission to improve literacy rates in underserved communities. We’ve highlighted key events where your participation will make an exceptional difference.”
For Project Management: Original Content: “Here’s the technical specification document for the project.”
Enhancement Prompt: “Add a brief executive summary at the beginning that explains the business benefits in non-technical language.”
Enhanced Output: “Executive Summary: This project aims to significantly decrease customer wait times while also reducing operational costs. The technical improvements outlined in this document directly address the key customer pain points identified in our recent satisfaction survey, without requiring additional staffing resources.”
By systematically enhancing existing content, you can leverage these assets more effectively, ensuring every document serves both immediate operational needs and broader strategic communication goals.
Leveraging Copilot as a Strategic Business Asset
For forward-thinking organisations, Copilot represents more than just a productivity tool—it’s a strategic asset that can transform how you develop solutions, communicate with stakeholders, and scale your business operations:
- Save Time: Create documents, emails, and presentations faster without sacrificing quality
- Improve Communication: Generate clearer explanations of complex topics for different audiences
- Focus on What Matters: Spend less time drafting and editing, and more time on strategic work. When implemented with clear purpose and strategy, Copilot becomes a powerful extension of your team’s capabilities, enabling more informed decisions and enhancing your ability to deliver exceptional value to clients.
Taking the Next Step: Strategic Implementation
Mastering these approaches to Copilot usage can significantly enhance your team’s productivity while ensuring consistent, high-quality output across all business activities.
If you’re interested in exploring how Copilot can be integrated into your broader technology strategy, our team is available to help you determine your Copilot readiness aligned with your business objectives and growth plans.
“Sorry, I was on mute!”
If this phrase has become part of your company’s unofficial vocabulary, you’re not alone.
Remote work has transformed from a temporary emergency response to a competitive advantage that attracts top talent worldwide. But there’s a stark difference between companies simply allowing remote work and those truly excelling at it.
The true challenge? Creating a seamless environment that enables productivity, fosters genuine human connection, and ensures secure access to critical systems—all without the physical office space.
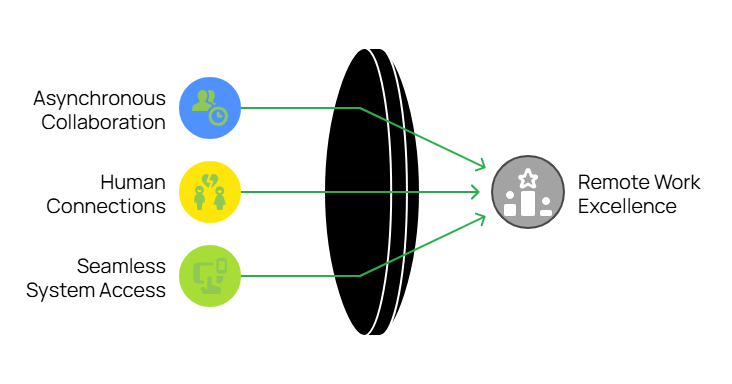
Three Pillars of Remote Work Excellence
1. Mastering Asynchronous Collaboration
For dispersed teams, especially those spanning multiple time zones, asynchronous work is essential. It allows team members to contribute meaningfully without being online simultaneously.
Practical strategies you can implement today:
- Visual task management that works: Microsoft Planner (included in Microsoft 365) provides intuitive Kanban boards, checklists, and progress tracking to keep everyone aligned regardless of location. Marketing teams can manage campaigns while allowing contractors to contribute on their own schedules.
- Collaborative documents without the chaos: Microsoft 365’s real-time editing and commenting features enable teams to provide real-time feedback and build on ideas without scheduling yet another meeting. The Track Changes and threaded comments preserve context for everyone.
- Asynchronous video messaging: Microsoft Teams allows team members to record and share short video messages directly in chats—perfect for explaining complex concepts or demonstrating processes without coordinating schedules.
Microsoft Teams allows team members to record and share short video messages directly in chats—perfect for explaining complex concepts or demonstrating processes without coordinating schedules.
Pro tip: For more detailed screen recordings, consider Loom as a complementary tool for step-by-step process documentation.
2. Building Real Human Connections
Without the natural interactions of office life, remote teams risk becoming disconnected. Deliberate strategies to foster genuine connections are crucial to prevent your team from feeling like “faceless, task-based robots.”
Connection-building strategies that work:
- Video-first communication: Make video the default for all meetings. This simple change dramatically increases engagement and understanding through non-verbal cues.
- “One remote, all remote” policy: If even one team member joins remotely, have everyone join via their individual devices. This creates an equal playing field and prevents remote workers from feeling like unimportant participants.
- Team huddles with purpose: Quick, energetic team check-ins foster a rhythm of collaboration and a sense of belonging. At Grassroots IT, our 25-member team, spanning five countries, connects daily through structured huddles. On Mondays, Wednesdays, and Fridays, we come together as a full team, while smaller operational check-ins drive focus on other days. Each session kicks off with reflections on our wins and challenges, cultivating an atmosphere of mutual support and connection.
- Inject fun strategically: Weekly team quizzes using tools like Kahoot! create shared experiences and friendly competition that builds camaraderie.
- Celebrate wins and milestones: Microsoft Viva makes it easy for team members to share successes and personal achievements. We use customised posts to celebrate positive client feedback, ensuring everyone feels valued regardless of location.
Real-world insight: Don’t underestimate the power of embracing your unique team culture. Something as simple as an enthusiastically off-key “Happy Birthday” sing-along during team huddles can become a cherished tradition that strengthens bonds.
3. Providing Seamless System Access
The foundation of productive remote work lies in ensuring equal and secure access to essential company resources. Without seamless access, frustration builds, communication falters, and workflows stall. By prioritising robust and user-friendly access solutions, companies empower their teams to remain connected, collaborative, and focused on their goals.
Tools for frictionless system access:
- Azure Virtual Desktop (AVD): Create a complete Windows desktop environment in the cloud, ideal for:
- Legacy applications that don’t perform well over distributed internet connections
- Graphics-intensive workflows requiring significant processing power
- Industries with strict data compliance requirements that need sensitive information kept secure in the cloud
- Microsoft Intune for comprehensive device management: Ensure all company devices stay updated and secure, with the ability to remotely wipe lost or compromised equipment regardless of physical location.
- Teams Calling integration: Allow employees to use their work phone numbers from anywhere through Microsoft Teams, maintaining professional communication whether they’re at home, in a café, or on the road.
Success story: One of our financial clients uses Azure Virtual Desktop to enable their team in the Philippines to work with complex spreadsheets while keeping sensitive customer data stored securely in Australia—simultaneously addressing performance, compliance, and collaboration needs.
Transforming Remote Work Challenges into Strategic Advantages
The shift to remote and hybrid work presents challenges, but with the right IT strategies, your business can create a collaborative environment that attracts top talent and drives growth regardless of geography.
By implementing these three pillars—asynchronous workflows, meaningful human connections, and seamless system access—you’ll build a remote work environment that empowers your team to perform at their best, wherever they are.
Ready to elevate your remote work strategy? The experts at Grassroots IT can help you implement these solutions tailored to your specific business needs. Contact us today to transform these insights into actionable plans that drive your business forward.
Looking for more guidance on optimising your remote work environment? Reach out to our team or explore our Microsoft 365 solutions designed specifically for the modern distributed workplace.
Every resource should fuel your nonprofit’s mission. But let’s be honest—outdated IT systems slow you down, consuming time and energy that should be focused on achieving your core purpose.
When technical issues prevent volunteers from accessing files or staff face constant system crashes, it creates a ripple effect hindering your ability to serve your community effectively.
By transforming outdated systems into modern, reliable solutions, your nonprofit can stop wrestling with technology and start amplifying your impact, driving your mission forward with confidence and efficiency.
The Challenge of Legacy IT in Nonprofits
Understanding the full scope of legacy IT challenges is crucial for nonprofits seeking to maximise their impact. These issues often create interconnected problems that compound over time, affecting every aspect of your operations.
Here’s how these challenges manifest:
1. Impacts on Mission Delivery
- Program Disruptions: Unstable infrastructure leads to service delivery interruptions and hampers community engagement.
- Limited Remote Capabilities: Outdated systems restrict volunteer participation and limit the effectiveness and reach of your programs.
- Inefficient Systems: Time-consuming processes reduce the time available for core mission activities.
2. Security & Compliance Risks
- Outdated Security Measures: These put sensitive donor and beneficiary data at risk.
- Unmanaged Devices: These create risk and are vulnerable points in your network.
- Poor System Integration: This compromises data protection and compliance efforts.
3. Operational Inefficiencies
- Manual Processes: Time-consuming tasks drain staff and volunteer resources.
- Limited Cloud Access: This hampers collaboration and flexibility.
- Aging Hardware and Software: They create daily frustrations and delays.
Every dollar spent on IT should advance your mission, not hold it back. Addressing these challenges proactively through a strategic IT approach can transform technology from a daily burden into a powerful tool that amplifies your nonprofit’s impact.
Why IT Transformation Matters for Nonprofits
Technology transformation isn’t just about fixing what’s broken—it’s about creating new possibilities for your organisation. When implemented strategically, IT becomes a powerful tool for advancing your mission. Here’s how strategic IT transformation can revolutionise your nonprofit’s operations:
1. Resource Optimisation:
Using the latest OS and application suite eliminates the constant drain of managing outdated systems, allowing your team to focus on what truly matters:
- Elimination of tech-related disruptions that waste valuable time
- More energy and focus available for core mission activities
- Smarter allocation of both human and financial resources
2. Enhanced Capabilities:
Up-to-date systems provide the tools your team needs to work efficiently and securely:
- Streamlined workflows and seamless collaboration across teams
- Faster, more reliable service delivery to your community
- Comprehensive security measures that protect sensitive donor and beneficiary information
3. Organisational Benefits:
The ripple effects of using cloud-based software like Microsoft 365 extend throughout your entire organisation:
- Higher staff satisfaction and retention through reliable tools
- Flexible remote and hybrid work options that expand your talent pool
- Increased organisational agility to adapt to changing community needs
These strategic improvements don’t just solve today’s problems—they create a foundation for sustainable growth and increased community impact for years to come. By investing in modern IT infrastructure, you’re investing in your nonprofit’s ability to serve more effectively and respond to new opportunities.
Real-world example: How our client shed years of Legacy IT and boosted efficiency
One of our clients, a nonprofit organisation dedicated to supporting migrant communities, faced years of stagnancy due to outdated IT infrastructure and lack of a digital strategy. The organisation relied on aging software and computers, limited cloud storage, poor cybersecurity, and inefficient systems that hindered productivity. Staff grappled with managing data, accessing files remotely, and delivering essential services effectively, this led to ongoing frustrations and operational challenges.
The Problem:Our client faced interconnected challenges that impacted their mission delivery:
- Core Infrastructure Issues:
- Aging software and computer systems
- Limited cloud storage capabilities
- Poor cybersecurity posture
- Inefficient systems hindering productivity
- Operational Impact:
- Staff struggling with basic data management
- Difficulty accessing files remotely
- Multiple user accounts causing confusion
- Frequent system disruptions affecting service delivery
- Time wasted on manual processes
- Limited ability to support remote work
The Solution: Our client prioritised improvements based on strategic goals and potential impact, working to implement several key initiatives such as:
- Identity and Access Management:
- Integrated legacy Active Directory with Azure AD
- Implemented single sign-on for unified user access
- Platform & infrastructure upgrades:
- Upgraded core network components
- Outdated endpoints were refreshed to obtain supported and secure machines.
- Implemented Microsoft Intune for device management
- Enhanced Security:
- Deployed Sophos firewalls
- Implemented secure VPN with mandatory MFA
- Enabled BitLocker encryption
- Conducted cybersecurity awareness training
The Result: Within 12 months, the organisation achieved significant improvements:
- System stability achieved after years of persistent issues
- 75% reduction in support tickets through proactive problem resolution
- Enhanced security posture through systematic gap remediation
- Improved employee efficiency with modern devices and applications
- 20+ hours per week saved through process automation
- Simplified access to resources through cloud integration
Steps to Begin Your IT Transformation
If your nonprofit is facing similar tech challenges, here are the actionable steps to get started:
1. Review Your Current IT Landscape
- Look at how your current technology helps or hinders your daily work
- List any outdated systems and security gaps
- Note which manual tasks are taking up too much time
2. Identify Your Organisation’s Needs
- Evaluate key workflows and consider what technology can support your mission.
- Consider needs like remote work, data management, or faster processes
- Focus on tools that will support your mission. Such as Improved data analytics?
3. Create a Transformation Plan
Develop a realistic roadmap for updating your systems. Focus on prioritising high-impact changes, such as implementing cloud systems or improving network security.
4. Get Expert Advice
Partner with an IT expert who truly understands the unique needs of nonprofits, offers dependable guidance, and ensures a smooth transition. Ideally this provider will also work as an extension of your team, be sensitive to your cause and understand your Non-profits unique needs and vision.
5. Train Your Team
Assess the varying levels of technological understanding among your volunteers and staff to identify their specific needs and areas for improvement. Offer hands-on training sessions tailored to different skill levels and provide ongoing support to ensure everyone feels confident using the tools and systems required for their roles.
6. Monitor and Optimise
IT transformation isn’t a one-time project—it’s an ongoing journey that requires constant attention and adaptation. To stay ahead, regularly review your systems to ensure they remain efficient and up to date. Gather feedback from both staff and clients to understand pain points and identify areas for improvement. Seek professional guidance when necessary to navigate complex challenges or implement new technologies. Finally, fine-tune your processes and tools where needed to keep your organization agile and aligned with evolving goals. Consistent effort is key to long-term success.
Investing in Change
Modernising IT systems can seem like a daunting task, but the potential return on investment—in terms of time saved, cost efficiency, and increased organisational impact—is significant.
Why is this so critical? Outdated IT infrastructure can hold back an organisation’s ability to grow and adapt. Upgrading your systems isn’t just about improving technology—it’s about creating a strong foundation that empowers your nonprofit to achieve its goals with greater precision and impact.
Need help transforming your IT? Contact us for tailored solutions and start driving real change today.
Moving to the cloud promises better efficiency, scalability, and cost savings – yet for growing businesses, the transition isn’t always smooth sailing. Many businesses reach this point because their current systems are becoming expensive and difficult to maintain. Server replacements, software updates, and constant maintenance drain both time and money. Cloud migration offers a way out of this cycle – but only if it’s done right.
Here are some of the common pitfalls we’ve encountered helping Australian businesses migrate to the cloud, and more importantly, how to avoid them.
1. Rushing Without a Strategy
When you’re running a busy operation, it’s tempting to rush straight into a cloud migration, especially if you’ve got staff crying out for better systems. Yet treating migration as a purely technical exercise almost always leads to headaches down the track.
One unfortunate situation that we sometimes see is companies attempting to migrate to SharePoint without sufficient planning. Rushing the migration process without comprehensive preparation often leads to a host of operational disruptions and complex technical challenges, including:
- Poor understanding of existing data landscapes
- Complexities of unmanaged network infrastructures
- Unexpected network throttling that disrupts data access and the migration process
- Temporary inaccessibility of critical business data both locally and in the cloud
- Significant difficulties for the client’s team in locating and effectively navigating newly migrated files
These experiences underscore the substantial risks inherent in accelerated migration strategies that prioritise speed over systematic, thoughtful implementation. The consequences highlight the critical importance of comprehensive planning, technical assessment, and strategic data mapping in successful SharePoint migrations.
A more successful approach is to start with a clear plan that puts your business needs first. You don’t need a complex strategy—just a clear understanding of what your team needs to work efficiently, and a staged approach that won’t overwhelm your staff.
2. Underestimating the True Costs
For mid-sized businesses, unexpected costs can hit hard. A Cloud migration isn’t just about the upfront project costs or monthly subscription fees – you need to consider staff training, potential network upgrades, and hidden setup costs.
A successful approach that we recommend is to start with a pilot program. Many businesses begin by moving just their email to the cloud first. This helps to provide a clear understanding of the real costs and challenges involved before committing to a full migration. From there, you can plan your full Microsoft 365 rollout in stages that match your cashflow and team’s capacity to adapt.
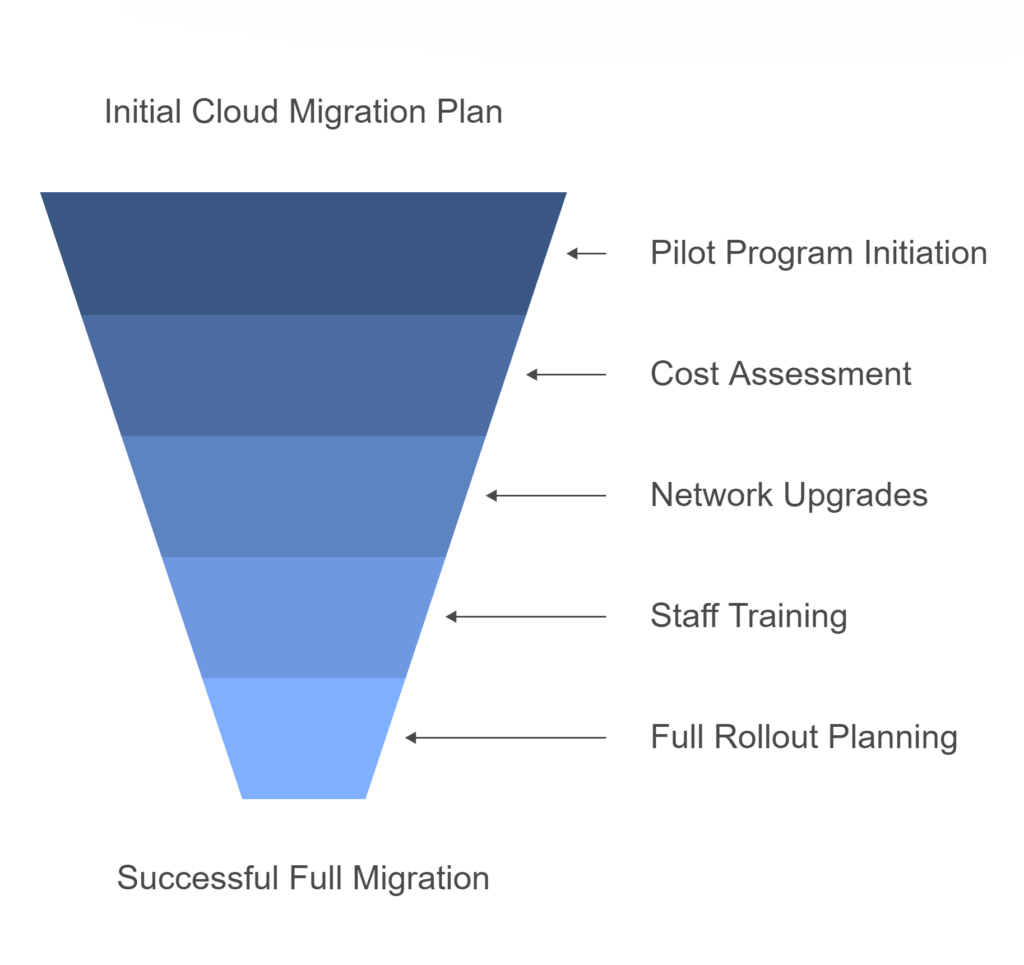
3. Poor Change Management
In a business where everyone knows each other, change management might seem unnecessary. But successful migrations depend on proper preparation and communication. Your team needs to understand what’s changing and why it matters to their daily work.
A proven approach is identifying two or three naturally tech-savvy staff members to become your migration champions. Give these team members early access to test new systems and help their colleagues adapt. This peer-to-peer support often makes the difference between resistance and enthusiasm.
4. Inadequate Security Planning
Many business owners assume moving to the cloud automatically makes everything secure. While platforms like Microsoft 365 are indeed secure by design, they still need proper setup and management to meet your unique needs.
The best approach here is to start with the fundamentals: strong passwords and Multi-Factor Authentication for everyone. Then focus on basic data protection policies – like preventing accidental external file sharing. You don’t need enterprise-grade security from day one, but you do need the basics done right.
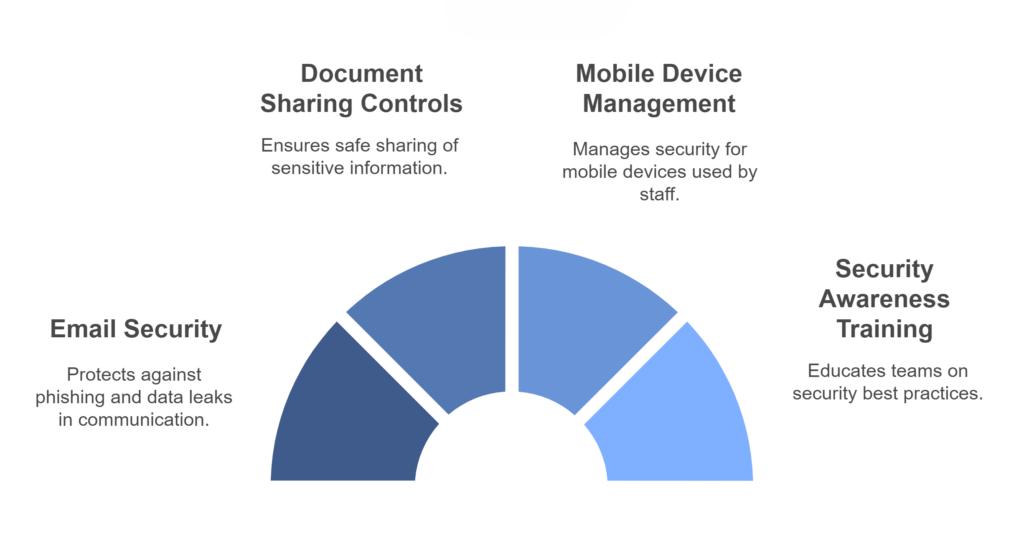
Data security in the cloud requires ongoing attention. Key areas to focus on include:
- Email security to prevent phishing attacks and data leaks
- Document sharing controls to protect sensitive information
- Mobile device management for staff using phones and tablets
- Regular security awareness training for your team
The goal isn’t to lock everything down but to find the right balance between security and usability for your business.
5. Not Planning for Business Continuity
When your whole team relies on cloud systems to work, any disruption hits hard. A recent example involved a client that faced challenges when two SharePoint libraries were deleted, without an adequate disaster recovery system in place. Although the data was restored, it no longer had the original file permissions or structure. This took several days to fix, reducing team productivity and requiring one resource to be fully dedicated to resolving the issue.
A smart approach to business continuity is setting up automated backups from day one and regularly testing your recovery process. Schedule data migrations during quiet periods and always have a way to quickly revert changes if needed.
Your business continuity plan should cover three key scenarios:
- System outages: Have clear procedures for what staff should do if they can’t access cloud systems
- Data loss: Maintain backups of critical business data with tested recovery procedures
- Access issues: Keep local copies of essential information like emergency contacts and basic procedures
Remember that cloud systems, while highly reliable, aren’t immune to disruption. The key is being prepared without being paranoid.
Moving Forward Successfully
Cloud migration doesn’t need to be overwhelming. With the right planning and support, businesses your size can transition smoothly and start enjoying the benefits sooner. The key is working with a partner who understands the practical challenges of moving a mid-sized business to the cloud.
Your Cloud Migration Checklist:
1. Document your current systems and what needs to move
2. Set a realistic budget and timeline
3. Plan your security essentials
4. Train your team
5. Test and verify backups
Ready to explore how cloud migration could work for your business? Our team has helped numerous businesses your size successfully transition to the cloud. Contact Grassroots IT today for a practical, no-obligation discussion about your needs.
You’ve probably heard the phrase “if it ain’t broke, don’t fix it” – but when it comes to your business technology, this mindset can lead to serious problems. Let me explain why.
Every technology change in your business carries some level of risk, whether it’s updating software, adding new hardware, or tweaking system settings. The key is understanding which changes need formal oversight and which can proceed through standard processes.
How we assess risk – Impact vs Likelihood
At Grassroots IT we assess the risk of any technology change by looking at two key factors. First, what would happen if something went wrong? We consider how many users would be affected, whether it would stop critical business processes, and how long recovery might take.
Second, we evaluate the likelihood of issues arising based on the complexity of the change, whether it’s been done before, and any known compatibility concerns.
Most low-risk changes can proceed through normal support channels. Updating a single user’s monitor or installing standard software updates are routine, well-understood, and easily reversed if needed, and generally don’t need to go through the formal change control process.
But when either the impact or likelihood of issues increases, that’s when formal change control becomes crucial. Think of changes like:
- Server upgrades
- Network reconfigurations
- Business-critical software updates
- Changes affecting multiple users or locations
The Change Advisory Board (CAB)
For significant changes, we bring together the Change Advisory Board – think of it as your technology brains trust. This group can typically include key stakeholders from your business, our technical experts who understand your systems, and project managers and team leaders who can coordinate the work. Their job is to review proposed changes, challenge assumptions, identify risks that might have been missed, and ensure the change plan is solid. It’s like an insurance policy against expensive mistakes.
What about Emergencies?
Sometimes we need to act fast – like when there’s a critical security patch for an active threat. For these situations, we have streamlined emergency procedures that allow rapid response while maintaining basic control measures. We always follow up with a thorough review to ensure everything went well and to document lessons learned for future reference.
The Change Control Process

Our change control process follows these key steps:
1. Request & Planning:
We begin by documenting exactly what needs to change and why. This includes identifying systems affected, expected benefits, and potential business impacts. Importantly, we also develop a roll-back plan, which is crucial for reverting any changes if unforeseen issues arise during implementation. Clear documentation here prevents misunderstandings later.
2. Risk Assessment:
Our team evaluates the potential risks and complexity of the proposed change. We consider factors like service disruption, data integrity, security implications, and resource requirements. This helps determine the level of control needed.
3. Review & Approval:
The change is reviewed by appropriate stakeholders – from technical specialists to business leaders, depending on the impact. High-risk changes go through our Change Advisory Board for additional scrutiny.
4. Implementation:
The change is carried out according to the approved plan, typically during predetermined maintenance windows to minimise business disruption. We maintain constant communication throughout this phase.
5. Verification:
We thoroughly check that the change achieved its objectives and didn’t cause any unexpected issues. This includes testing affected systems and gathering feedback from users.
6. Documentation:
Finally, we update our system records and document any lessons learned. This builds our knowledge base for future changes and maintains a clear audit trail.
The Real Business Value
Good change control isn’t about bureaucracy – it’s about protection and business value. Changes are planned and communicated in advance, minimising surprises. Work happens outside core business hours when needed, reducing disruption. Everyone knows who’s doing what and when, providing clear accountability. And if something does go wrong, we can quickly restore things to normal.
The Bottom Line
Smart businesses understand that change control is essential for protecting operations while enabling progress. By matching the level of control to the level of risk, and maintaining streamlined procedures for urgent situations, you get the best of both worlds: careful control when possible, rapid response when needed.
Technology changes are inevitable. The question isn’t whether to manage them, but how well you’ll manage them. A robust change control process helps ensure those changes drive your business forward rather than hold it back.
More and more Australian organisations are discovering the strategic advantage of ISO 27001 certification. It’s exciting to see businesses of all sizes embracing this globally recognised security standard, opening doors to new partnerships and market opportunities. What was traditionally the domain of enterprise organisations has evolved into a powerful business enabler for growing companies across the country.
What’s ISO 27001 All About?
Strip away the fancy language, and ISO 27001 is simply an internationally recognised way to prove you’re serious about protecting information. While it might sound complex, at its heart it’s about having a systematic approach to keeping customer data safe, protecting your business from cyber threats, managing access to information, and being prepared when things go wrong. Think of it like a driver’s licence for information security – it proves you know what you’re doing and can be trusted to handle sensitive information properly.
Meeting ISO Requirements with Microsoft 365
The good news is that Microsoft 365 already includes a range of features that can directly support your journey to ISO 27001 compliance. Let’s look at exactly how you can use Microsoft 365 features to meet specific ISO requirements. Here’s your practical guide to ticking those ISO boxes using tools you already have.
User Access Management
What ISO Requires
The standard demands formal processes for managing user access throughout the entire employee lifecycle. This control exists because inappropriate access rights are a major security risk – think ex-employees with active accounts, or staff with more system access than they need. ISO wants to see that you’re actively managing these risks through formal processes and regular reviews. You need a systematic way to grant, modify, and revoke access based on people’s roles, ensuring everyone has exactly what they need to do their job – nothing more, nothing less.
Real-world example
- When Sarah from Accounts leaves, all her access needs to be removed within 24 hours
- When Jim moves from Support to Sales, his system access needs to change to match his new role
- Every quarter, managers need to confirm their team members still need their current access levels
- When Dave from IT needs admin access to fix an urgent issue, it should be time-limited and logged
How to Meet It with Microsoft 365
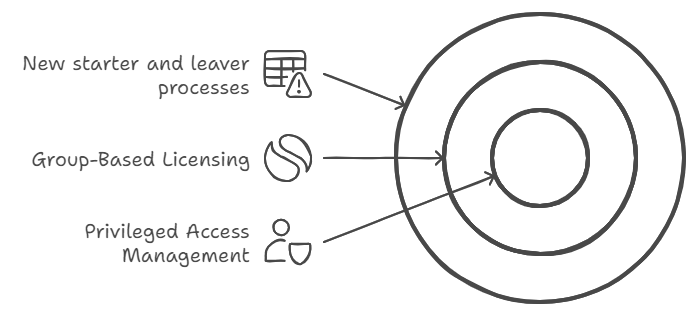
1. For new starter and leaver processes:
- Set up automated workflows in Azure AD: When HR marks an employee as terminated, their accounts are automatically disabled
- Configure group-based licensing: New sales staff automatically get Salesforce access, while marketing gets Adobe Creative Suite
- Use access reviews: Managers get quarterly emails to verify their reports still need access to sensitive data
- Enable Microsoft Groups expiration: Teams/SharePoint access automatically expires if not renewed
2. For privileged access management:
- Set up just-in-time access: IT staff request admin rights for 2 hours to perform maintenance
- Configure approval workflows: Senior IT approval required for global admin access
- Enable session recording: All admin activities in sensitive systems are logged
Authentication Controls
What ISO Requires
You need to prove you’re properly controlling system access. This requirement recognises that passwords alone aren’t enough anymore. ISO wants evidence that you’re using modern authentication methods to verify users’ identities, especially when accessing sensitive information or systems. It’s about making sure that even if someone gets hold of a password, they can’t automatically access your systems. The standard also emphasises the importance of protecting access information – like making sure password rules are strong enough and that you can detect and block suspicious login attempts.
Real-world examples:
- Jane shouldn’t be able to log in with just a password when accessing payroll data from home
- Failed password attempts should lock an account after 5 tries
- If Bob’s session is idle for 15 minutes, he should be logged out
- When Alice tries to log in from an unusual location, extra verification should be required
How to Meet It with Microsoft 365
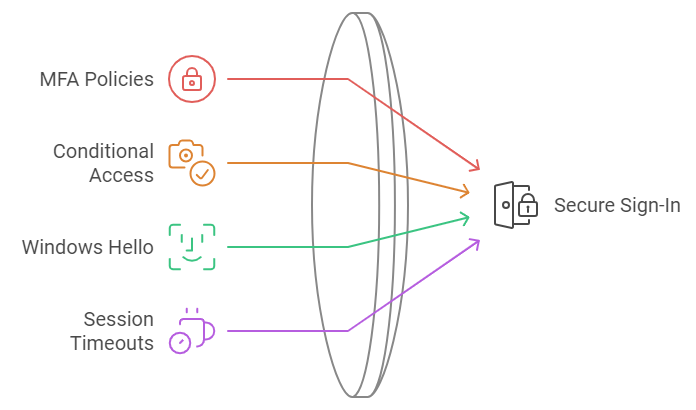
1. For secure sign-in:
- Configure MFA policies: Force additional verification for all remote access
- Set up Conditional Access: Require managed devices for accessing customer data
- Enable Windows Hello: Replace passwords with biometric login
- Configure session timeouts: Auto-logout after 15 minutes of inactivity
Information Classification
What ISO Requires
You must show that sensitive information is properly identified and protected. This control recognises that not all information needs the same level of protection – your marketing brochure doesn’t need the same security as your customer credit card details. ISO requires you to think through what types of information you handle, how sensitive each type is, and what protection it needs. Then you need to show that you’ve got systems in place to consistently identify and protect information based on its sensitivity level.
Real-world examples:
- Customer credit card details need the highest level of protection
- Internal project documents shouldn’t be shareable outside the company
- HR documents should only be accessible by the HR team
- Marketing materials can be widely shared but not modified by everyone
How to Meet It with Microsoft 365
1. For automatic classification:
- Create sensitivity labels: “Confidential-Finance”, “Internal-Only”, “Public”
- Configure auto-labelling: Documents with credit card numbers automatically marked as “Confidential”
- Set up visual markers: Confidential documents get a red header saying “Internal Use Only”
2. For information handling:
- Enable encryption: “Confidential” documents can only be opened by approved users
- Set up DLP: Block sharing of documents containing tax file numbers
- Configure SharePoint permissions: HR site only accessible by HR team members
Cryptographic Controls
What ISO Requires
Sensitive data must be properly encrypted. This requirement goes beyond just turning on encryption – ISO wants to see that you’ve thought through when and where encryption is needed, and that you’re managing it properly. This includes having formal policies about what needs to be encrypted, managing encryption keys securely, and making sure your encryption methods are strong enough for the sensitivity of the data you’re protecting. It’s about ensuring that if someone does get unauthorized access to your systems, they still can’t read your sensitive data.
Real-world examples:
- Client contracts must be encrypted when stored
- Financial reports being emailed to the board need encryption
- Mobile devices with company data must be encrypted
- Backup files need to be encrypted before going to cloud storage
How to Meet It with Microsoft 365
1. For data at rest:
- Enable BitLocker: All laptop drives automatically encrypted
- Configure SharePoint encryption: All documents encrypted with unique keys
- Set up Exchange mailbox encryption: Emails encrypted by default
2. For data in transit:
- Enable TLS: All email communications encrypted in transit
- Configure secure external sharing: Client portal access using encrypted connections
- Set up encrypted backup: Automatic encryption before cloud backup
Logging and Monitoring
What ISO Requires
ISO needs you to prove you’re actively monitoring your systems. This means having systems in place to detect, capture, and investigate security events and user activity. It’s not just about recording what happens – you need to show that you’re actively reviewing these records and can spot potential security incidents quickly. Think of it like CCTV for your IT systems – it needs to be recording, but someone also needs to be watching the monitors.
Real-world examples:
- All admin actions in key systems need to be logged and reviewable
- Failed login attempts need to be monitored and investigated
- File access patterns need to be tracked to spot unusual behaviour
- System changes need to be logged and attributable to specific users
How to Meet It with Microsoft 365
1. For audit logging:
- Enable Unified Audit Logging in Security & Compliance
- Configure alert policies for sensitive actions
- Set up log retention policies for compliance
2. For security monitoring:
- Enable Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps
- Configure alert policies for suspicious activities
- Set up automated incident reporting
Communications Security
What ISO Requires
Information needs to be protected whenever it’s being shared or moved around. This control focuses on keeping data safe when it’s in transit between systems or being shared with external parties. It’s about making sure sensitive information can’t be intercepted or tampered with when it’s moving between point A and point B, whether that’s within your network or out to external partners.
Real-world examples:
- Customer data being shared with partners needs encryption
- Confidential emails need to be protected from interception
- File transfers between systems need to be secure
- External collaboration needs to be controlled and monitored
How to Meet It with Microsoft 365
1. For email security:
- Enable Exchange Online Protection
- Configure anti-phishing policies
- Set up Safe Attachments and Safe Links
2. For secure file sharing:
- Configure SharePoint sharing policies
- Enable Teams external access controls
- Set up secure guest access policies
The Bottom Line
Getting ISO 27001 certified doesn’t mean buying new security tools. Microsoft 365 includes powerful features that map directly to ISO requirements – you just need to know what to turn on and how to configure it.
Need help setting up these controls or mapping them to your ISO requirements? That’s what we do. Let’s talk about getting your Microsoft 365 environment ISO-ready.
For small to medium-sized businesses, Microsoft 365 Business Premium offers a robust suite of productivity tools coupled with advanced security features. However, many organisations are not taking full advantage of the security capabilities included in their subscription. In this post, we’ll explore the key security features of Microsoft 365 Business Premium and how you can leverage them to protect your business.
Understanding Microsoft 365 Business Premium
Microsoft 365 Business Premium is more than just a productivity suite—it’s a comprehensive solution that combines the familiar Office applications with advanced security and device management capabilities. This license tier is often considered the “sweet spot” for small to medium-sized businesses, offering enterprise-grade features at a fraction of the cost.
Key Security Features in Microsoft 365 Business Premium
Let’s dive into the security features that come standard with your Business Premium license:
1. Microsoft Defender for Office 365 (Plan 1)
Microsoft Defender for Office 365 is a cloud-based email filtering service that helps protect your organisation against advanced threats like phishing and zero-day malware.
Key components include:
- Safe Links: This feature provides time-of-click verification of URLs in emails and Office documents. It helps protect your organisation by checking web addresses against a list of known malicious links.
- Safe Attachments: This feature checks email attachments for malicious content. It opens attachments in a virtual environment to detect malicious behaviour before delivering the email.
- Anti-phishing protection: Advanced machine learning models and impersonation detection help protect your users from phishing attacks.
Pro Tip: These features aren’t necessarily enabled by default, so make sure to activate them to take full advantage of their capabilities.
2. Intune Mobile Device Management
Intune is Microsoft’s mobile device management (MDM) and mobile application management (MAM) platform. It allows you to manage both company-owned and personal devices used to access company data.
Key benefits include:
- Enforce device-level security policies (e.g., requiring a PIN to unlock the device)
- Selectively wipe company data from lost or stolen devices
- Manage and deploy apps to devices
Pro Tip: Start with basic policies like requiring a device PIN and the ability to remotely wipe company data. Gradually introduce more advanced policies as your team becomes comfortable with the system.
3. Azure Information Protection (AIP)
AIP helps you classify, label, and protect sensitive information. It can automatically detect sensitive data types (like credit card numbers or health information) and apply appropriate protections.
Key features:
- Prevent sensitive information from being shared inappropriately
- Track and control how protected information is used
Pro Tip: Begin by identifying your most sensitive data types and creating policies to protect them. Educate your users on the importance of data classification and how to use the AIP tools effectively.
4. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA is one of the most effective ways to protect against unauthorised access. It requires users to provide two or more verification factors to gain access to a resource, significantly reducing the risk of compromised accounts.
Pro Tip: Implement MFA for all users, starting with administrators and gradually rolling out to all staff. Consider using the Microsoft Authenticator app for a seamless user experience.
5. Conditional Access Policies
Conditional Access allows you to control access to your resources based on specific conditions. You can create policies that grant or restrict access based on factors like user location, device status, and detected risk level.
Key use cases:
- Block access from countries where your business doesn’t operate
- Require MFA for access to sensitive applications
- Ensure only managed and compliant devices can access company resources
Pro Tip: Start with a few critical policies and gradually expand. Always test new policies in a limited pilot before full deployment.
6. Exchange Online Archiving
While primarily a compliance feature, Exchange Online Archiving contributes to security by helping you retain and protect important email data. It provides users with an archive mailbox for storing old email messages.
Key benefits:
- Automatic movement of old emails to the archive based on policies
- eDiscovery capabilities for legal or compliance needs
- Retention policies to ensure important data isn’t accidentally deleted
Pro Tip: Set up retention policies that align with your industry regulations and business needs. Train users on how to access and use their archive mailboxes effectively.
Case Study: Small Business Success with M365 Business Premium Security
One of our clients, a local mining company with 70 employees was struggling with security concerns, particularly around protecting client financial data. By implementing Microsoft 365 Business Premium and fully leveraging its robust security features, the company saw significant improvements:
- 90% reduction in phishing emails reaching user inboxes
- Zero data breaches in the 6 months following implementation
- Improved ability to meet industry compliance requirements
- Increased employee productivity due to reduced downtime from security incidents
- Streamlined device management using Intune Compliance and configuration policies
- Standardised app deployment to all users leveraging Intune app deployment policies.
- Improved access controls using Conditional Access policies to for Geo Location, User risk and MFA
The firm faced initial challenges with user adoption, particularly around MFA and Geo Location policies. However, with a comprehensive user training campaign, they achieved full adoption within three months.
Conclusion
Microsoft 365 Business Premium offers a wealth of security features that can significantly enhance your organisation’s cybersecurity posture. By fully leveraging these tools, you can protect your business against a wide range of threats while also improving productivity and compliance.
Remember, cybersecurity is not a one-time effort but an ongoing process. Regularly review and update your security measures to stay ahead of evolving threats.
How Grassroots IT Can Help
At Grassroots IT, we specialise in helping businesses make the most of their Microsoft 365 investments. Our team of experts can:
- Assess your current security posture and identify areas for improvement
- Develop a customised implementation plan for M365 Business Premium security features
- Provide user training to ensure smooth adoption of new security measures
- Offer ongoing support and optimisation of your Microsoft 365 environment
Don’t leave your business vulnerable. Contact us today for a consultation, and let’s explore how we can enhance your cybersecurity with Microsoft 365 Business Premium.
Grassroots IT, a leading provider of managed IT services, is proud to announce its recent achievement of three prestigious ISO certifications: ISO 9001, ISO 14001, and ISO 27001. This triple certification demonstrates our unwavering commitment to quality management, environmental responsibility, and information security.
Raising the Bar in IT Services
What These Certifications Mean for Our Clients
- ISO 9001 (Quality Management): This certification ensures that we have robust processes in place to consistently meet customer requirements and enhance satisfaction..
- ISO 14001 (Environmental Management): By achieving this standard, we demonstrate our commitment to minimising our environmental impact and contributing to sustainability.
- ISO 27001 (Information Security Management): This certification validates our systematic approach to managing sensitive company and customer information, ensuring its confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Looking Ahead
About Grassroots IT
Established in 2005, Grassroots IT delivers and supports Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Data & Automation solutions for small and mid-sized organisations. With a focus on collaborative partnerships and a people-first approach, we work as an extension of your team to deliver reliable, strategic IT solutions that drive business growth.
Traditional security measures, while still important, are no longer sufficient to protect your organisation from sophisticated attacks. Enter Conditional Access Policies: a powerful tool in the Microsoft 365 suite that can significantly enhance your cybersecurity posture. In this post, we’ll explore how these policies work and why they are becoming an essential component of modern cybersecurity strategies.
What are Conditional Access Policies?
Conditional Access Policies are a feature of Microsoft 365 that allows you to control access to your organisation’s resources based on specific conditions. Think of them as smart gatekeepers for your digital assets. Instead of a simple “yes” or “no” to access requests, these policies consider various factors before granting access, such as:
- Who is requesting access?
- Where are they accessing from?
- What device are they using?
- What level of risk is associated with the access request?
By evaluating these factors in real-time, Conditional Access Policies can make nuanced decisions about whether to grant access, deny access, or require additional verification.
Current State of Cybersecurity
It’s not hyperbole to say that cybersecurity threats are growing exponentially, so before we dive deeper into Conditional Access Policies, let’s consider the current cybersecurity landscape.
- Remote work has expanded the attack surface for many organisations
- Phishing attacks are becoming increasingly sophisticated
- Ransomware incidents are on the rise, with potentially devastating consequences
- Data breaches can result in significant financial and reputational damage
In this environment, a static, one-size-fits-all approach to security is no longer adequate. Organisations need dynamic, context-aware security measures that can adapt to different situations and threat levels.
5 Ways Conditional Access Policies Enhance Your Security
Let’s explore five keyways that Conditional Access Policies can dramatically improve your cybersecurity posture:
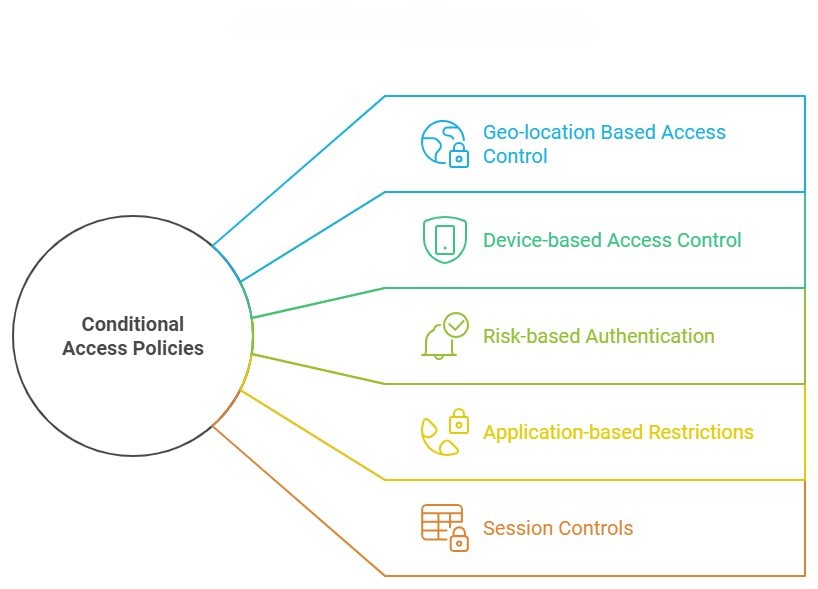
1. Geo-location Based Access Control
One of the most powerful features of Conditional Access Policies is the ability to restrict access based on geographic location.
How it works: You can set policies that only allow access from specific countries or regions where your business operates. Attempts to access your resources from other locations can be blocked or require additional verification.
Real-world example:
- The Problem: An Australian based Veterinarian practice was receiving consistent login attempts to Microsoft 365 accounts from multiple locations around the world, causing concerns for an account breach.
- The Solution: Conditional Access policies were implemented to restrict user access to countries the Veterinarian practice traded from and dedicated IP restrictions of selected accounts that only needed to be accessed from the practices.
- The Result: Significant decrease in malicious user login attempts from blocked countries, and no accounts breaches for accounts only accessible from the practices.
2. Device-based Access Control
Ensuring that only trusted devices can access your resources is another crucial aspect of cybersecurity.
How it works: Conditional Access Policies can be set to only allow access from devices that are managed by your organisation or that meet certain security requirements.
Why it matters: This prevents scenarios where an employee might access sensitive company data from a personal device that lacks proper security measures. It also mitigates risks associated with lost or stolen devices. This is particularly important in the context of your organisation’s BYOD policy.
3. Risk-based Authentication
Microsoft’s cloud intelligence can detect signs of suspicious activity, which Conditional Access Policies can use to adjust authentication requirements in real-time.
How it works: If a login attempt is flagged as high-risk (e.g., it’s from an unfamiliar location or shows signs of bot activity), the policy can require additional verification steps or block access entirely.
Why it’s powerful: This adaptive approach means that routine, low-risk activities aren’t disrupted, but potential threats are met with appropriate security measures.
Real-world example:
- The Problem: A Mining organisation had an incident that almost allowed a fraudulent financial transaction to be processed.
- The Solution: Several Conditional Access policies were implemented, including Risk based access control, which uses Microsoft 365 intelligence to review user login and determine if there is any risk associated with the login and the level of risk for the login.
- The Result: All key financial and admin users are now assessed for each login, with Microsoft 365 determining any risk associated with the login session. Several key finance staff who were working via VPN were blocked when their sessions were re-authenticated after the VPN was disconnected, resulting in high-risk behaviour being detected, their accounts being blocked, and a password change required on login to unlock the account.
4. Application-based Restrictions
Not all company resources are equally sensitive. Conditional Access Policies allow you to set different access requirements for different applications or data types.
How it works: You might set a policy that allows broad access to the company intranet but requires multi-factor authentication and a company-managed device to access financial systems.
Real-world example:
- The Problem: An education institute required user access to email, Teams and SharePoint to be limited to only Microsoft applications on personal devices, allowing for greater control of the data.
- The Solution: Conditional Access policies that specifically target any access form a personal device and restricting access on this device to Microsoft Apps only.
- The Result: All users accessing the education Institute data for a personal device were required to install the Microsoft Company Portal App to allow management of institute data on their devices and enforce all policies applied to personal devices. This resulted in the institute finding multiple mobile devices that did not have any unlock code and multiple users who were accessing data from non-Microsoft apps that were not manageable via MDM.
5. Session Controls
Conditional Access doesn’t stop working after the initial authentication. It can also control what users can do during their sessions.
How it works: Policies can be set to limit activities like downloading, printing, or copying data from certain applications, even after a user has been granted access.
Why it matters: This can prevent data exfiltration attempts, where a bad actor who has gained access tries to download large amounts of sensitive data.
Real-world example:
- The Problem: An educational institute required that user access to email, Teams chat, and SharePoint documents could not be saved on personal devices.
- The Solution: Conditional Access policies that specifically target any access form a personal device, implementing session controls to block saving on these devices.
- The Result: Users accessing institute data on personal devices was blocked from saving emails, Teams chat and SharePoint documents, users were required to download and install the Microsoft Company Portal app and verify their account. allowing session controls on personal devices and blocking saving data outside of approved Microsoft apps.
Case Study: How our Client Improved Their Security with Conditional Access
Let’s look at how one of our clients, a mid-sized financial services firm, leveraged Conditional Access Policies to enhance their security:
Before implementing these policies, Company X had experienced several minor security incidents, including a case where an employee’s credentials were used to access company data from overseas during a time when the employee wasn’t traveling.
We helped them implement a comprehensive set of Conditional Access Policies, including:
- Geo-location restrictions
- Device management requirements
- Risk-based authentication
The result? In the six months following implementation:
- Suspicious access attempts decreased by 90%
- There were zero successful unauthorised access incidents
- Employee reports of account lockouts due to forgotten passwords decreased, thanks to the more nuanced, risk-based approach
While the IT team initially worried about user pushback, they found that most employees appreciated the additional security, especially once they understood how it protected both the company and their own personal information.
Conclusion
In an era where cyber threats are constantly evolving, static security measures are no longer enough. Conditional Access Policies provide a dynamic, intelligent approach to cybersecurity that can dramatically improve your organisation’s security posture.
By implementing these policies, you can:
- Reduce your risk of data breaches
- Gain greater control over how and where your company resources are accessed
- Adapt your security measures in real-time to respond to potential threats
- Improve overall compliance with data protection regulations
Remember, cybersecurity is not a one-time effort, but an ongoing process. Regularly reviewing and updating your Conditional Access Policies should be a key part of your overall security strategy.
How Grassroots IT Can Help
At Grassroots IT, we specialise in helping businesses leverage the full power of Microsoft 365, including advanced security features like Conditional Access Policies. Our team of experts can:
- Assess your current security posture
- Design and implement Conditional Access Policies tailored to your specific needs
- Provide ongoing support and optimisation of your policies
- Train your team on best practices for cybersecurity
Don’t wait for a security incident to occur. Take proactive steps to protect your organisation today. Contact us for a consultation, and let’s explore how we can enhance your cybersecurity with Conditional Access Policies.